Greeting (Part I): Run a Task with an API Route
Continuing the quick start tutorial, we will now learn how to invoke a task with an actual trigger.
-
To create a data process and an API route trigger, and have the data process to read payload data from the trigger, parse the name and generate a greeting response.
-
Learn how to pass data in and out of the session storage and cast them to user-defined data structures.
-
Execute the data process as a task using the API route and view its execution result.
Data Process Design
Logic
| Logic | Type | Name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Generic | Greeting | Parse the name field from payload as a Person data structure and write it into the session storage. |
| #2 | Aggregator | Greeting Aggregator | Get Person from session storage and finalise the task result with a greeting message with the name. |
Trigger
| Type | HTTP Method | Path |
|---|---|---|
| API Route | GET | /tutorial/greeting |
Task Payload
{
"name": "Arthur Dent"
}
Task Result
{
"status": "ok",
"taskId": "...",
"message": "Hello, Arthur Dent!"
}
Create and Build Logic
See: Create an Entry File and Build a Logic From an Entry File
Create and build two logic as you've learned in Quick Start.
Generic Logic: Greeting
The Person Parser (person-parser.*) generic logic is responsible for the following steps:
- Read the API route payload. Throw an error or Exception if it is not a HTTP payload from an API route.
- Parse the payload body to a
Personobject (with or without an explicitly defined type) containing only thenamefield. - Write the
Personobject into the session storage.
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
- C#
import { LoggingAgent, SessionStorageAgent } from "@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk";
/** @param {import('@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk').GenericContext} ctx */
export async function run(ctx) {
// load payload
const payload = await ctx.payload();
// throw an error if payload is not from API route
if (!("http" in payload))
throw new Error("this logic requires HTTP payload");
// read payload body
const data = payload.http.request.data;
// try to parse body to JSON
let parsed = null;
if (data) {
try {
parsed = JSON.parse(new TextDecoder().decode(new Uint8Array(data)));
} catch (e) {
LoggingAgent.error(
`failed to parse HTTP payload to JSON: ${e.message}`,
);
}
}
// create Person object
/** @type {{ name: string; }} */
const person = {
name: parsed?.name || "User",
};
LoggingAgent.info({
person: person,
});
// write Person into session storage
await SessionStorageAgent.putJson("person", person);
}
/**
* @param {import('@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk').GenericContext} ctx
* @param {import('@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk').RailwayError} error
*/
export async function handleError(ctx, error) {
LoggingAgent.error(error.message);
}
import {
GenericContext,
LoggingAgent,
RailwayError,
SessionStorageAgent,
} from "@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk";
// Person interface
interface Person {
name?: string;
}
export async function run(ctx: GenericContext) {
// load payload
const payload = await ctx.payload();
// throw an error if payload is not from API route
if (!("http" in payload))
throw new Error("this logic requires HTTP payload");
// read payload body
const data = payload.http.request.data;
// try to parse body to JSON
let parsed = null;
if (data) {
try {
parsed = JSON.parse(new TextDecoder().decode(new Uint8Array(data)));
} catch (e) {
LoggingAgent.error(
`failed to parse HTTP payload to JSON: ${e.message}`,
);
}
}
// create Person object
const person: Person = {
name: parsed?.name || "User",
};
LoggingAgent.info({
person: person,
});
// write Person into session storage
await SessionStorageAgent.putJson("person", person);
}
export async function handleError(ctx: GenericContext, error: RailwayError) {
LoggingAgent.error(error.message);
}
using System.Text;
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
// Person class
internal class Person
{
[JsonPropertyName("name")]
public string? Name { get; set; }
public Person(string name = "User")
{
Name = name;
}
public override string ToString() => $"Person: {name}";
}
// Source Context class for Person
[JsonSourceGenerationOptions()]
[JsonSerializable(typeof(Person))]
internal partial class PersonSourceGenerationContext : JsonSerializerContext
{
}
public static class Logic
{
public static async Task Run(Context ctx)
{
// load payload
var payload = await ctx.GetPayload();
// throw an exception if payload is not from API route
if (payload.Http is null)
{
throw new Exception("this logic requires HTTP payload");
}
// read payload body
byte[] data = payload.Http.Request.Data;
// create a Person object with default name
Person person = new();
// try to parse body to JsonNode
if (data.Length > 0)
{
try
{
person = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<Person>(
Encoding.UTF8.GetString(data),
PersonSourceGenerationContext.Default.Person
);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
await LoggingAgent.Error(
$"failed to parse HTTP payload to JSON: {e.Message}!"
);
}
}
await LoggingAgent.Info($"person = {person}");
// write Person into session storage
await SessionStorageAgent.Put(
"person",
StorageValue.FromJson(
person,
PersonSourceGenerationContext.Default.Person
)
);
}
public static async Task HandleError(Context ctx, Exception error)
{
await LoggingAgent.Error(error.Message);
}
}
Aggregator Logic: Greeting Aggregator
The Greeting Aggregator (greeting-aggregator.*) aggregator is similar to the one in Quick Start, except that it will
- Read the
Personobject from the session storage. - Generate a task result containing a greeting message, which will include the
namefield ofPerson.
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
- C#
import {
LoggingAgent,
ResultAgent,
SessionStorageAgent,
} from "@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk";
/** @param {import('@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk').AggregatorContext} ctx */
export async function run(ctx) {
// read Person from session storage
/** @type {{ name: string; }} */
const person = (await SessionStorageAgent.get("person")) || {
name: "User",
};
LoggingAgent.info(`person = Person: ${person.name}`);
// finalise task result
ResultAgent.finalize({
status: "ok",
taskId: ctx.task.taskKey.taskId,
message: `Greetings, ${person.name}!`,
});
}
/**
* @param {import('@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk').AggregatorContext} ctx
* @param {import('@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk').RailwayError} error
*/
export async function handleError(ctx, error) {
// finalise task result with error
ResultAgent.finalize({
status: "error",
taskId: ctx.task.taskKey,
message: error.message,
});
}
import {
AggregatorContext,
LoggingAgent,
RailwayError,
ResultAgent,
SessionStorageAgent,
} from "@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk";
// Person interface
interface Person {
name?: string;
}
export async function run(ctx: AggregatorContext) {
// read Person from session storage
const person: Person = (await SessionStorageAgent.get("person")) || {
name: "User",
};
LoggingAgent.info(`person = Person: ${person.name}`);
// finalise task result
ResultAgent.finalize({
status: "ok",
taskId: ctx.task.taskKey.taskId,
message: `Greetings, ${person.name}!`,
});
}
export async function handleError(ctx: AggregatorContext, error: RailwayError) {
// finalise task result with error
ResultAgent.finalize({
status: "error",
taskId: ctx.task.taskKey,
message: error.message,
});
}
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Text.Json.Nodes;
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
// Person class
internal class Person
{
[JsonPropertyName("name")]
public string? Name { get; set; }
public Person(string name = "User")
{
Name = name;
}
public override string ToString() => $"Person: {name}";
}
// Source Context class for Person
[JsonSourceGenerationOptions()]
[JsonSerializable(typeof(Person))]
internal partial class PersonSourceGenerationContext : JsonSerializerContext
{
}
public static class Logic
{
public static async Task Run(Context ctx)
{
// read Person from session storage
JsonNode? data =
(await SessionStorageAgent.Get("person"))?.JsonValue;
// create a Person object with default name
Person person = new();
// convert JsonNode to JSON string and parse to Person
if (data is not null)
{
person = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<Person>(
data,
PersonSourceGenerationContext.Default.Person
);
}
await LoggingAgent.Info($"person = {person}");
// finalise task result
var task = await ctx.GetTask();
await ResultAgent.SetResult(
new JsonObject()
{
["status"] = "ok",
["taskId"] = task.TaskKey.TaskIdString(),
["message"] = $"Greetings, {person.name}!"
}
);
}
public static async Task HandleError(Context ctx, Exception error)
{
// finalise task result with error
var task = await ctx.GetTask();
await ResultAgent.SetResult(
new JsonObject()
{
["status"] = "error",
["taskId"] = task.TaskKey.TaskIdString(),
["message"] = error.Message
}
);
}
}
Create Data Process
After creating and building both logic successfully, create a data process containing the People Parser and Greeting Aggregator logic.
Create API Route
See: Create an API Route
After creating the data process, create an API route with the following configuration:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| API Route Name | Greeting |
| HTTP Method | POST |
| URL | /tutorial/greeting |
| Request Mode | Sync |
| Response Content Type | JSON |
| Encapsulation | True |
| API Tasks | Data Process Greeting (latest revision) |
The full API route URL will be https://{LOC server}/tutorial/greeting that accepts POST Requests.
Invoke API Route
See: Invoke an API Route
After creating an API route, wait a moment for LOC to deploy it, then use a HTTP client to invoke the API route with the following JSON body (with Content-Type set to application/json if necessary):
{
"name": "Arthur Dent"
}
For example, using curl:
curl -X POST -d '{
"name": "Arthur Dent"
}' 'https://{LOC server}/tutorial/greeting'
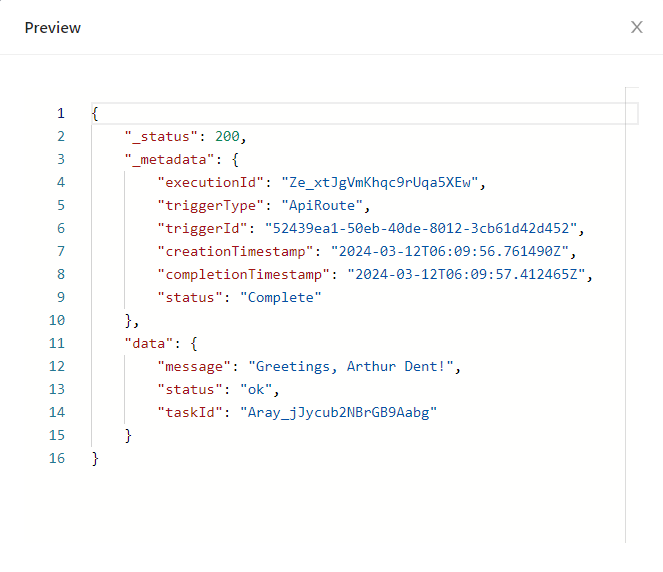
The API route, once invoked successfully, should return a HTTP response that contains a body similar to below:
{
"_status": 200,
"_metadata": {
"executionId": "Ze_xtJgVmKhqc9rUqa5XEw",
"triggerType": "ApiRoute",
"triggerId": "52439ea1-50eb-40de-8012-3cb61d42d452",
"creationTimestamp": "2024-03-12T06:09:56.761490Z",
"completionTimestamp": "2024-03-12T06:09:57.412465Z",
"status": "Complete"
},
"data": {
"message": "Greetings, Arthur Dent!",
"status": "ok",
"taskId": "Aray_jJycub2NBrGB9Aabg"
}
}
The task responded to our input with a greeting message containing the name we've gave it.
View Trigger Response and Execution Result
For viewing more detailed information of the execution, copy the execution ID (Ze_xtJgVmKhqc9rUqa5XEw) from the result above and use it to search the corresponding execution result in Studio.
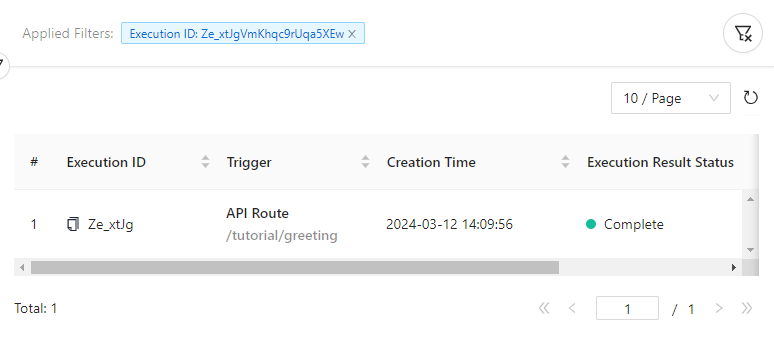
Click API Route /tutorial/greeting to inspect the full execution result:
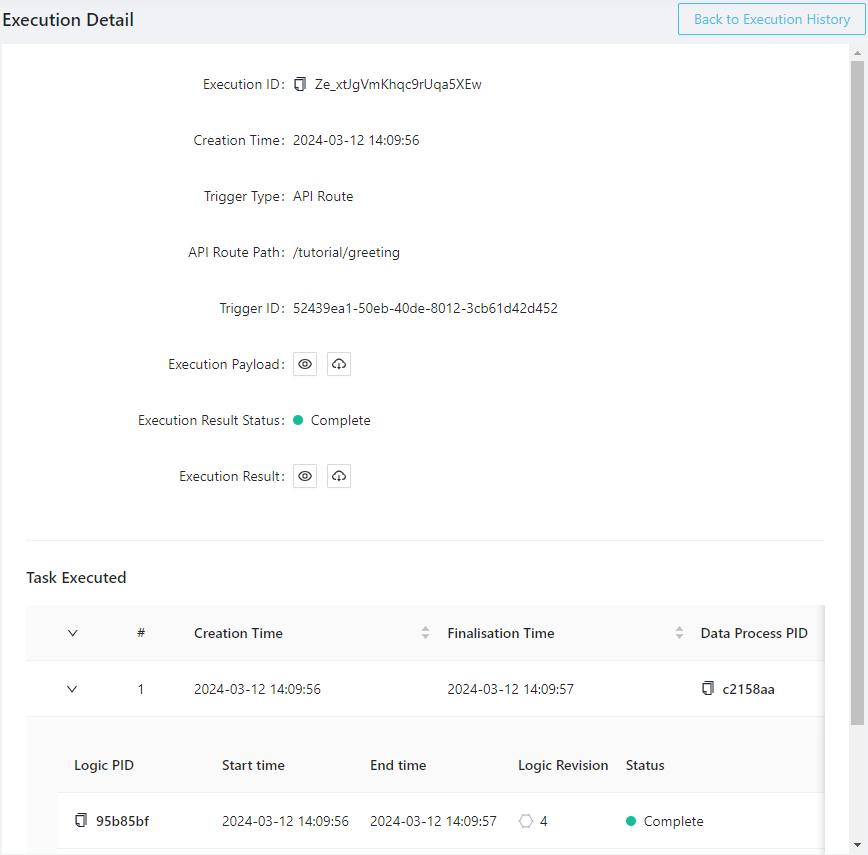
Click the icon behind Execution Result to inspect the response body, which is the same as the one we've received via the HTTP client: