Create and Deploy Data Process
See Introduction and Setup first if you haven't gone through the steps above.
Also refer to LOC Feature Overview to learn more about LOC features, especially the hierarchy of projects, scenarios, data processes and logic.
In this article we'll see how to create and deploy a data process (as well as the project, scenario and associated logic) using LOC CLI.
Some actions require logged in since they would read or operate remote assets:
- Build logic
- Edit data process (to link deployed logic)
- Deploy project
See CLI Command Reference to knnow more about CLI commands.
Workspace Structure Overview
From CLI v0.8.0, the new CLI workspace would look like this:
/[local workspace]
/.loc
/projects
projects.yaml <-- metadata of all projects, scenarios and data processes
logic-manifest.yaml <-- metadata of logic
/generic-logic-source <-- directory of generic logic source code
logic-1.js
logic-2.js
logic-3.ts
logic-4.ts
...
/aggregator-logic-source <-- directory of aggregator logic source code
aggregator-1.js
aggregator-2.ts
...
.locignore <-- files to be ignored during deploy
loc <-- CLI binary
package.json <-- local NPM package information
Unlike in v0.7.0 and previous versions, logic (source logic files) are now created and stored separately - and to be linked into data processes afterwards - while data processes are stored as metadata under projects and scenarios.
Deploy Logic
Create a Logic
Here we'll use the Quick Start tutorial as our example. First create the Payload JSON Parser generic logic (CLI will prompt you for various fields and options):
> ./loc logic create
✔ Logic Name · payload-json-parser
✔ Logic Type · Generic
✔ Programming Language · JavaScript
All Logic source files will be placed under "generic-logic-source" where you can create your own sub-directory. For example: giving "mylogic/convertJSON.js" will create a new sub-directory under "generic-logic-source"
✔ Entrypoint File Path · payload-json-parser.js
✔ Description for Logic · Payload JSON parser
Successfully create Generic Logic source file at "generic-logic-source/payload-json-parser.js"
Create the other two logic in the same way (be minded that one of them is an aggregator logic.)
Now in ./loc/logic-manifest.yaml should contains three new logic metadata entry:
version: v0
logics:
- permanentIdentity: null
name: payload-json-parser
description: ""
type: Generic
spec:
JavaScript:
entrypointFilePath: generic-logic-source/payload-json-parser.js
- permanentIdentity: null
name: greeting
description: ""
type: Generic
spec:
JavaScript:
entrypointFilePath: generic-logic-source/greeting.js
- permanentIdentity: null
name: result-aggregator
description: ""
type: Aggregator
spec:
JavaScript:
entrypointFilePath: aggregator-logic-source/result-aggregator.js
Do not manually edit any files under the .loc sub-directory!
Which points the new logic metadata to the new source files. The logic do not have permanent IDs yet, which are assigned by LOC and are required for linking logic into a data process, so we need to deploy them.
Deploy Logic to LOC
Now build and upload the logic we've just created:
> ./loc logic build
Select a Logic to build.
? LOGIC TYPE PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE NAME PERMANENT IDENTITY ENTRYPOINT FILE PATH DESCRIPTION
═════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
❯ Generic JavaScript payload-json-parser <null> generic-logic-source/payload-json-parser.js Payload JSON parser
Generic JavaScript greeting <null> generic-logic-source/greeting.js Hello World greeting
Aggregator JavaScript result-aggregator <null> aggregator-logic-source/result-aggregator.js Result aggregrator
Select the generic logic to build. After a very short while you should see the following message:
Build 1 logic successfully!
LOGIC TYPE NAME PERMANENT IDENTITY REVISION DESCRIPTION
══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
Generic Payload JSON Parser 5864162f-e163-4a5c-b9f7-f3bc503132c1 1 Payload JSON parser
Run the command again to build/upload the aggregator logic as well.
Check ./loc/logic-manifest.yaml and you should see both logic are assigned with an unique ID:
version: v0
logics:
- permanentIdentity: 5864162f-e163-4a5c-b9f7-f3bc503132c1
name: payload-json-parser
...
- permanentIdentity: d31255ee-6ef4-4390-bd70-846b9ea8b675
name: greeting
...
- permanentIdentity: 4bd3c39f-a137-423e-885b-d4159fbd29a2
name: result-aggregator
...
You can also build and upload all logic at once:
./loc logic build --all
If a logic is already deployed, run loc logic build will not upload a new revision of it.
Create Project, Scenario and Data Process
In order to link logic into a data process, we'll need to create the following assets.
New Project
> ./loc project create
✔ Name of Project · my-cli-project
✔ Description of Project · My CLI project
New Scenario
> ./loc scenario create
Select Project of Scenario
Select Project of Scenario
? PROJECT NAME DESCRIPTION CREATED TIME
══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
❯ my-cli-project My CLI project 2023-03-29 16:06:51.312136500 UTC
✔ Name of Scenario · my-cli-scenario
✔ Description of Scenario · My CLI scenario
Successfully create Scenario my-cli-scenario
New Data Process
> ./loc dp create
Select Project
✔ PROJECT NAME DESCRIPTION
═══════════════════════════
my-cli-project My CLI project
Select Scenario
✔ SCENARIO NAME DESCRIPTION
═════════════════════════════
my-cli-scenario My CLI scenario
✔ Data Process Name · hello-world
✔ Data Process Description · Hello World tutorial
Successfully create Data Process hello-world
Checkout Project and Scenario
For the convenience of creating a data process under a given project and scenario, we can "checkout" them as below:
> ./loc checkout my-cli-project my-cli-scenario
Switch current project/scenario to my-cli-project/my-cli-scenario.
The checkout action does not affect any local nor remote assets. This is merely creating a shortcut so you don't have to repeatly select a project and a scenario.
To cancel current checkout, run
./loc checkout --reset
Link Deployed Logic into Data Process
In order to link logic to the data process, we need to edit it:
> ./loc dp edit
Select Data Process
✔ PERMANENT IDENTITY DATA PROCESS NAME REVISION LINKED LOGICS PROJECT
══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
<null> hello-world 1 0 my-cli-project
✔ New Data Process name · hello-world
✔ New Data Process description · Hello World tutorial
Data Process: hello-world
Generic Logic
<No Generic Logic linked to Data Process>
Aggregator Logic
<No Aggregator Logic linked to Data Process>
(`e` to edit, or press enter to skip)
If you did not checkout a project and a scenario with loc checkout, CLI will prompt you to select them.
You'll have the options to modify the name and description of the data process. The last section shows there are currently no logic in this data process.
Now press e to enter the logic edit menu:
? Choose your next move ›
❯ Add Generic Logic
Edit Generic Logic
Unlink Generic Logics
Add/Edit Aggregator Logic
Unlink Aggregator Logic
Save
Exit
We select our deployed generic logic into the first slot:
✔ Choose your next move · Add Generic Logic
[1/4] Add Generic Logic - Choose Position
Move cursor to where you want to insert Generic Logic, press enter to continue
By default, Logic will be inserted right below chosen one except first logic slot
? PERMANENT IDENTITY LOGIC NAME REVISION ORDER
════════════════════════════════════════════
❯ <first logic slot>
[2/4] Add Generic Logic - Pick Generic Logic
Move cursor to select which Generic Logic you want to add
? PERMANENT IDENTITY LOGIC NAME REVISION ORDER
══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
...
❯ 5864162f-e163-4a5c-b9f7-f3bc503132c1 payload-json-parser 1
[3/4] Add Generic Logic - Pick Generic Logic Revision
Move cursor to select which Generic Logic revision you want to use
═══════════════════════════════════════════════════
PERMANENT IDENTITY | 5864162f-e163-4a5c-b9f7-f3bc503132c1 |
═══════════════════════════════════════════════════
? REVISION LOGIC NAME DESCRIPTION
═════════════════════════════════════════════
❯ 1 payload-json-parser Payload JSON parser
If there are existing generic, select <first logic slot> will add the new logic in front of it. Select the existing logic will add the new logic behind it, for example, for linking the greet logic:
✔ Choose your next move · Add Generic Logic
[1/4] Add Generic Logic - Choose Position
Move cursor to where you want to insert Generic Logic, press enter to continue
By default, Logic will be inserted right below chosen one except first logic slot
? PERMANENT IDENTITY LOGIC NAME REVISION ORDER
══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
<first logic slot>
❯ 5864162f-e163-4a5c-b9f7-f3bc503132c1 Payload JSON Parser 1 1
If the logic has multiple revisions existing on LOC server, CLI will also prompt you to select one.
After adding the generic logic, you can add the aggregator logic in the exact same way:
Aggregator Logic
<No Aggregator Logic linked to Data Process>
? Choose your next move ›
Add Generic Logic
Edit Generic Logic
Unlink Generic Logics
❯ Add/Edit Aggregator Logic
Unlink Aggregator Logic
Save
Exit
Finally select save:
? Choose your next move ›
Add Generic Logic
Edit Generic Logic
Unlink Generic Logics
Add/Edit Aggregator Logic
Unlink Aggregator Logic
❯ Save
Exit
✔ Choose your next move · Save
Successfully update Data Process: hello-world
Inspect the Edited Data Process
You can open .loc/projects/projects.yaml under the workspace to inspect how projects, scenarios and data processes metadata are saved:
projects:
- name: my-cli-project
description: My CLI project
creation_timestamp: 2023-03-29T16:06:51.312136500Z
unit_id: 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000
scenarios:
- name: my-cli-scenario
description: My CLI scenario
creation_timestamp: 2023-03-29T16:07:27.550192100Z
project_ref:
ref_tag: name
ref: my-cli-project
dataProcesses:
- revision: 1
name: hello-world
description: Hello World tutorial
genericLogics:
- permanentIdentity: 5864162f-e163-4a5c-b9f7-f3bc503132c1
revision: 1
logicVariables: {}
agentConfiguration:
database:
agents: []
fileStorage:
agents: []
http:
agents: []
mail:
agents: []
- permanentIdentity: d31255ee-6ef4-4390-bd70-846b9ea8b675
revision: 1
logicVariables: {}
agentConfiguration:
database:
agents: []
fileStorage:
agents: []
http:
agents: []
mail:
agents: []
aggregatorLogic:
permanentIdentity: 4bd3c39f-a137-423e-885b-d4159fbd29a2
revision: 1
logicVariables: {}
enabled: true
timeout: null
explorerPath: ""
creation_timestamp: 2023-03-29T16:07:58.804966Z
tag_ids: []
scenario_ref:
ref_tag: name
ref: my-cli-scenario
You can see that this is a manifest of the interlinking assets, including metadata for each data processes - logic variables, agent configurations and tasks, etc.
Since CLI v0.8.0, during the current porting process from TypeScript to Rust, does not yet support managing the following assets from local workspace:
- Tags and units
- Triggers (API route, message queue and scheduler)
- Agent configuration
- License
The API route, agent configuration, tags and license features are available in LOC Studio.
Deploy Project, Scenario and Data Process
To upload the data process, we need to deploy the whole project. This will upload and update the project with its scenarios/data processes onto LOC:
> ./loc project deploy
✔ PROJECT NAME DESCRIPTION CREATED TIME
═════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
my-cli-project My CLI project 2023-03-29 16:06:51.312136500 UTC
Deploy Project: my-cli-project...
Deploy Scenarios...
Deploy Data Processes...
Successfully deploy Project!
CLI will still prompt you to select a project even if you have checkout one with loc checkout.
If you take a look at .loc/projects/projects.yaml again, you'll see all of the assets now have an assigned unique ID:
projects:
- id: d0e930e6-80b1-4e76-8c6c-c65c517cd9dc
server:
name: my-cli-project
description: My CLI project
creation_timestamp: 2023-03-29T16:20:49.678856Z
unit_id: 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000
local: null
deleted: false
scenarios:
- id: c8b0e85a-a214-4402-9b5f-855786df54b6
server:
name: my-cli-scenario
description: My CLI scenario
creation_timestamp: 2023-03-29T16:20:50.059126Z
project_ref:
ref_tag: id
ref: d0e930e6-80b1-4e76-8c6c-c65c517cd9dc
local: null
deleted: false
dataProcesses:
- permanent_identity: 8fc20e9a-5c8d-486a-b1c5-b897a6c99f16
server: ...
We have successfully deploy a project with one scenario and one data process with three linked logic. The deployed assets will appear in Studio as well with the logic labeled as "Native" logic:
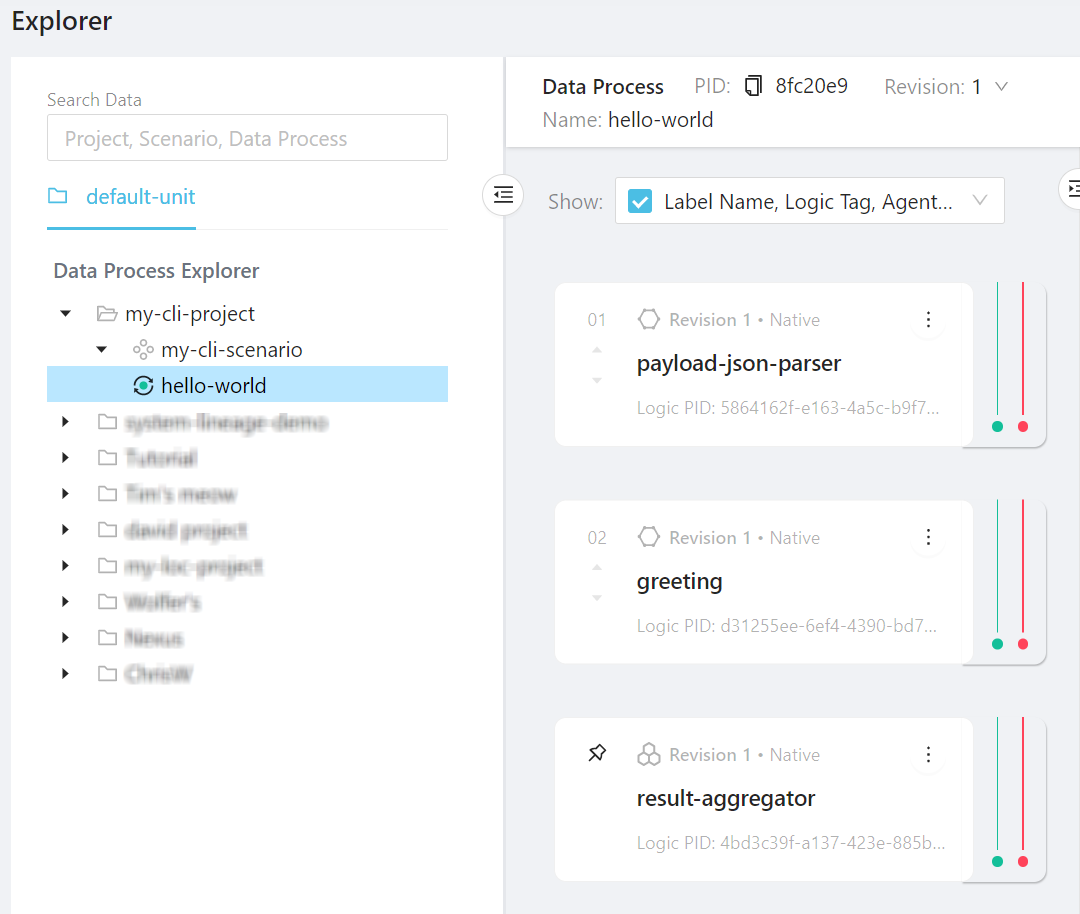
See Source and Version Control to learn more about project synchronisation in CLI.
Create Shared Libraries and Types
You can create shared (utility) custom libraries as JavaScript or TypeScript scripts for multiple logic. They will be compiled together when the logic are built and uploaded.
For example, we often have to use TextDecoder to decode Uint8Array array to string. We can hence create a /utils/utils.js with the following content:
// shared helper function
const UTF8ArrToStr = (aBytes) => {
const utf8decoder = new TextDecoder();
return utf8decoder.decode(new Uint8Array(aBytes));
};
// export functions
export { UTF8ArrToStr };
Then import it into a project's logic:
...
// import UTF8ArrToStr
import { UTF8ArrToStr } from "../utils/common";
export async function run(ctx) {
const payload = await ctx.payload();
const data = payload.http.request.data;
// calling the utility function
const parsed = JSON.parse(UTF8ArrToStr(data));
const name = parsed?.name; // assuming there is a name field
// ...
}
For TypeScript developers, you can also share type definitions using a .ts module, which is very useful to enforce type check across TypeScript logic:
// now it's called common.ts
...
// shared custom type, which defines a JSON object's shape
type UserName = {
name: string;
}
// export type
export { ..., UserName };
Then import it into a .ts logic:
import { ..., HttpPayload } from "@fstnetwork/loc-logic-sdk";
...
// import UTF8ArrToStr
import { ..., UserName } from "../utils/common";
export async function run(ctx) {
...
// calling the utility function and use custom type
const parsed: UserName = JSON.parse(UTF8ArrToStr(data));
const name = parsed.name; // now name will be inferred as string in IDE
// ...
}